Sputtering Recommended Products

TP3090
The output voltage is continuously adjustable from 0 to 20kV ,The output frequency is...
View Products

THP2350
Output Voltage 20kV ,Output Power 5kW ,0.1% p-p ripple ,Fast recover、low arc current...
View Products
TP3090 Photoelectric Converter
Photoelectric converter, TTL signal is converted into optical signal
View Products
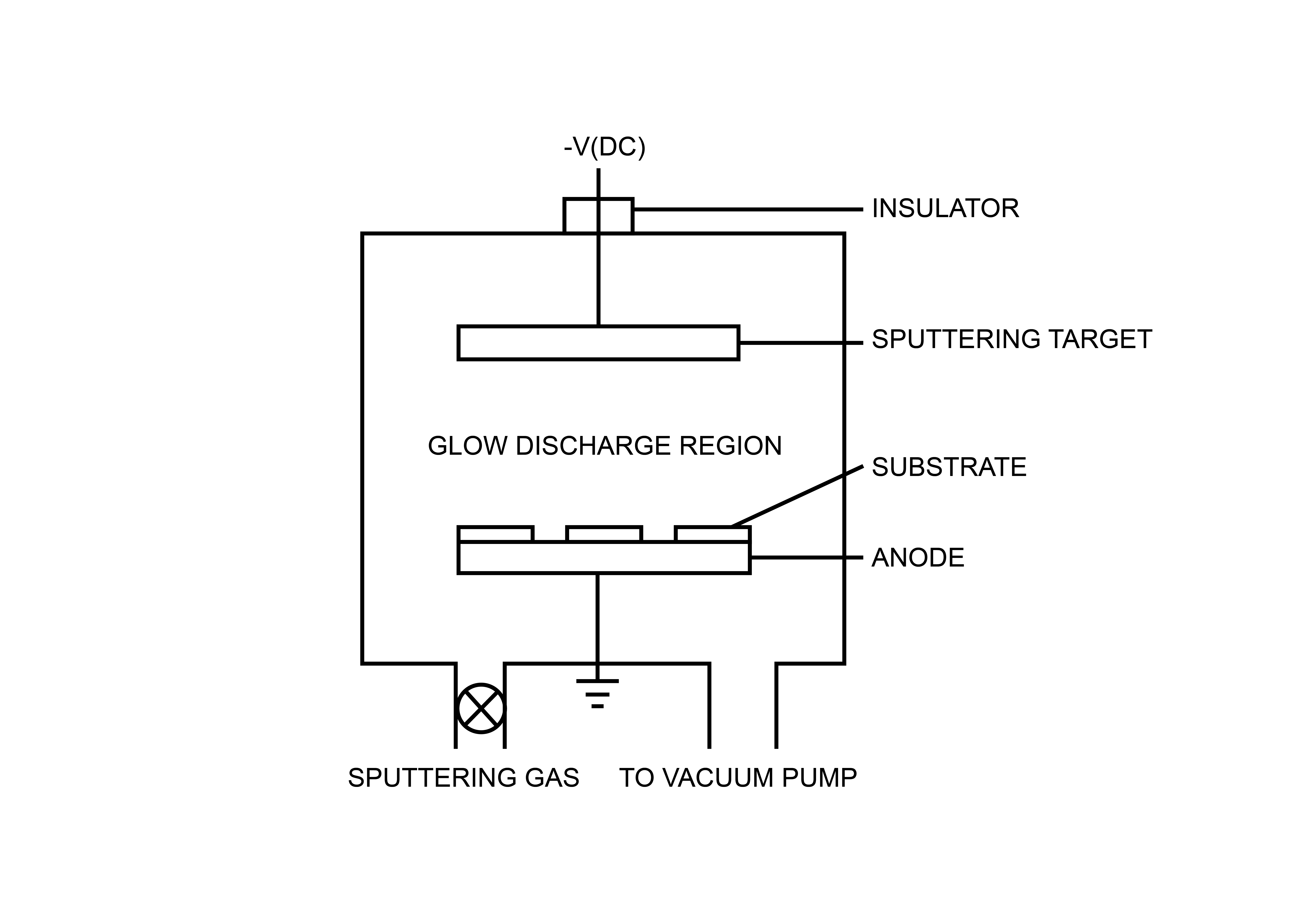
Sputtering
Sputtering is a process that uses charged particles to bombish a target material, causing atoms or molecules on the surface of the target to escape and deposit on the substrate to form a film. This technology is widely applied in fields such as semiconductor manufacturing, disk coating, and architectural glass coating. Direct current sputtering is mainly used for sputtering metal targets (such as gold, silver, copper, aluminum, titanium, etc.) and some alloy targets with good electrical conductivity. Reactive sputtering involves introducing reactive gases (such as oxygen or nitrogen), where the atoms of the target material react chemically with the gas molecules to form compound films (such as alumina or titanium nitride). This method is often used for targets with poor electrical conductivity

















