Electrostatic oiling Recommended Products
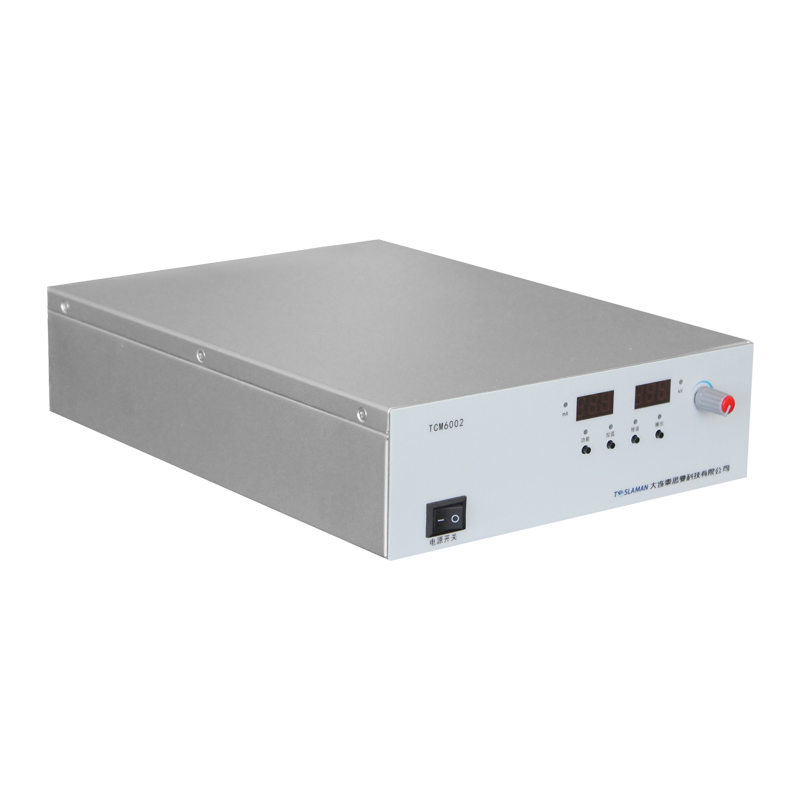

TCM6002
Maximum Output Voltage 50kV, Adjustable ,Maximum Output Current 3mA ,Maximum Output ...
View Products
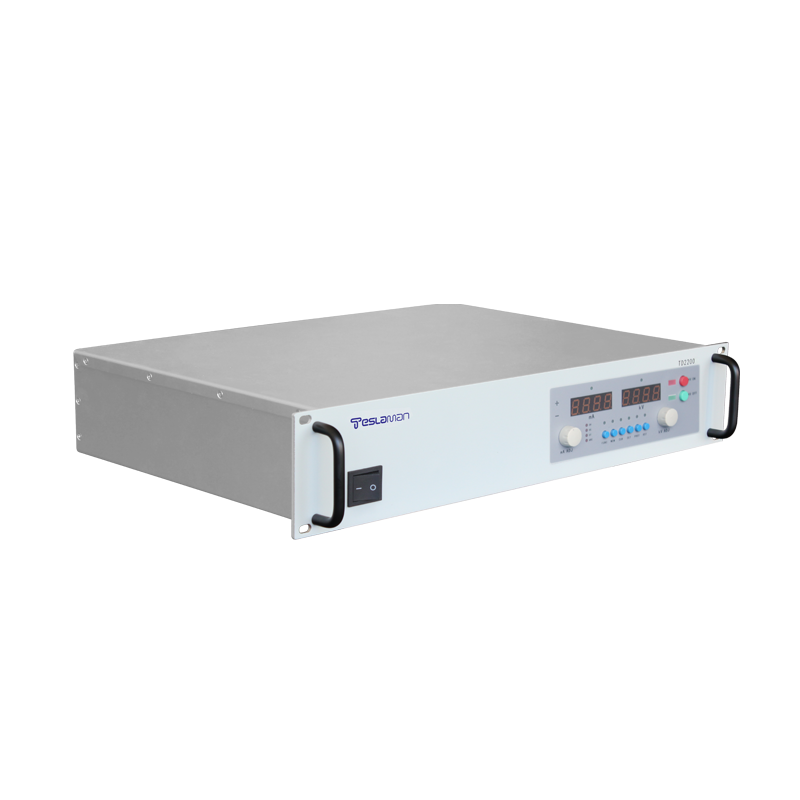

TD2200
Soft Switching ,Output Voltage 1kV-100kV ,Output Power 600W ,Digitally Programmable ...
View Products
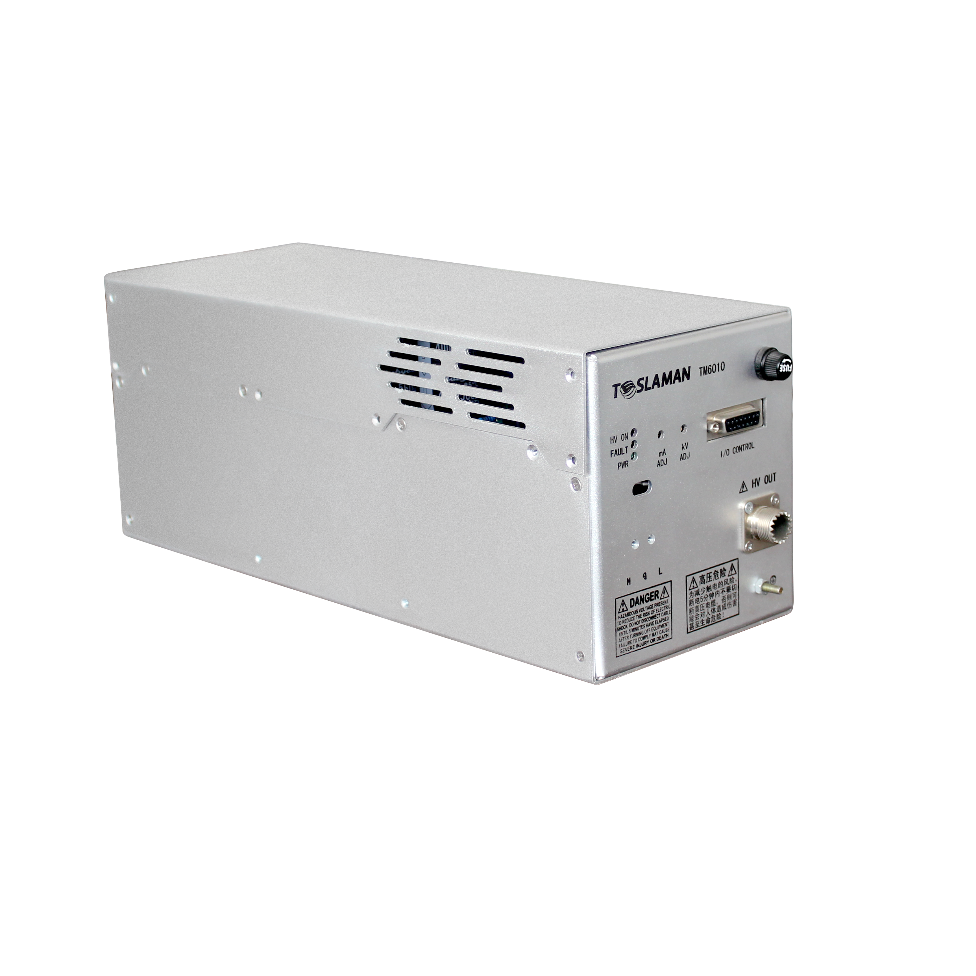

TM6010
Output Voltage 1kV-100kV ,Output Power 1kW ,Nanosecond Protection Response ,Over-Volt...
View Products
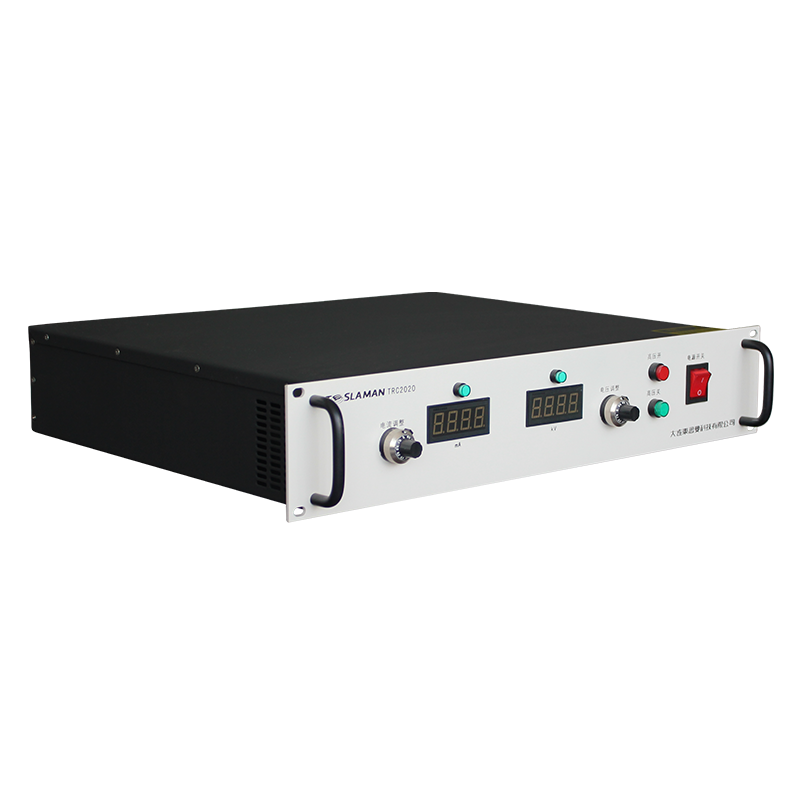

TRC2020
Output Voltage 1kV-100kV ,Maximum Output Power 300W ,Digital Voltage and Current Dis...
View Products

TRC2025
Output Voltage 1kV-100kV ,Output Power 500W-1kW ,Over-Voltage, Over-Current, Short Cir...
View Products
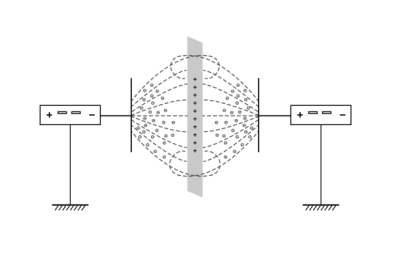
Electrostatic oiling
Electrostatic oiling application primarily relies on electrostatic principles to uniformly deposit rust-preventive oil onto target surfaces, such as galvanized steel sheets. In this process, the upper and lower knife beams within the oiler act as electrodes, typically set at negative polarity and connected to a high negative voltage, while the galvanized sheet is grounded to serve as the positive electrode. Consequently, a high-voltage electrostatic field is established between the knife beams and the galvanized sheet. The rust-preventive oil inside the knife beams becomes polarized and acquires a negative charge, forming tiny negatively charged oil droplets. Under the influence of the electric field, these oil droplets travel along the electric field lines towards the positively charged galvanized sheet and discharge upon deposition, forming a uniform oil film on its surface.

















